Pharma exports in India soar, despite cough syrup deaths
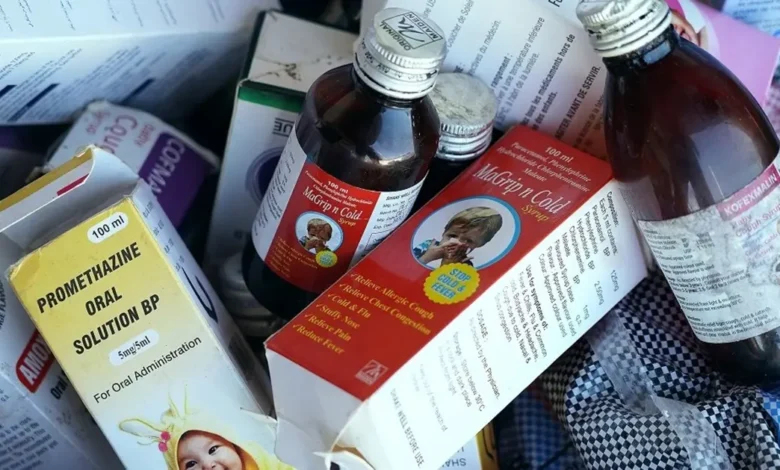
India’s pharmaceutical exports this fiscal year are set to grow nearly twice as fast as last year to hit sales of $27 billion, driven by strong US buying, a government-backed trade body told Reuters, despite deaths linked to Indian-made cough syrups.
The robust forecast comes against the backdrop of earlier concerns from the government that last year’s deaths of dozens of children in Gambia, which the World Health Organization (WHO) linked to drugs made in India, had “adversely impacted the image of India’s pharmaceutical products across the globe.”
Two other cough syrups made in India killed 19 children in Uzbekistan around December, according to the Uzbekistan government.
India is the world’s third largest maker of drugs by volume after the United States and China, and senior pharma trade official Udaya Bhaskar said the country was too big a player for buyers to move away because of “these aberrations” in Gambia and Uzbekistan.
“As far as the Gambia and Uzbekistan incidents are concerned, if you see in terms of the image of the country, there is a dent,” Bhaskar, director general of the Pharmaceuticals Export Promotion Council of India (Pharmexcil), told Reuters on Tuesday.
“But if you see our (April-June) exports, they have grown. We are doing very well in the US market, we are growing at more than 10 percent there. In the past four-five months, the growth in exports shows that people have not taken very, very seriously (any concerns about) the quality of Indian pharmaceuticals.”
India’s pharma exports rose 3.25 percent in the year to March 31 to $25.4 billion and Bhaskar said it was set to grow by about 6.3 percent to $27 billion this fiscal year.
Sales to the United States, India’s biggest market with 30 percent of its overall pharma exports, rose 6.2 percent to $7.5 billion last fiscal year, government data show.
India’s overall pharma exports in the April-June quarter rose 5 percent to $6.58 billion.
India is seeing good overall demand for drugs for central nervous system conditions, cardiovascular and oncology, Bhaskar said.
Country visits
Pharmexcil delegations have visited countries including Nigeria, Egypt and Russia in recent months to allay any concerns about Indian drugs, he said.
“Wherever we are going, people are asking and we are clarifying,” Bhaskar said. “We are telling them our stand. We are trying our level best.”
India has denied links to the deaths in Gambia but found another company guilty of sending adulterated products to Uzbekistan and cancelled its license. The company, Marion Biotech, has denied wrongdoing.
Gambia has made it mandatory for all Indian drugs to be tested before being exported to the African country since July 1. India has since June 1 made it compulsory for all cough syrups to be tested before export.
But India’s cough syrup exports, including those made by drugmakers that follow the traditional Indian method of Ayurveda, are only about $15 million a year and exports have largely remained intact, Bhaskar said.
Apart from Gambia, no other country has asked for additional tests for Indian drugs since the deaths, he said.
“Whatever exports we are doing to countries like the US, our largest importer, they are not asking. There are so many countries we are exporting to, the UK, South Africa, Brazil or any other market. They are not asking.”
Manufacturing a drug in Europe or the United States costs more than 30 percent than in India, giving India a big advantage, he said.
“India is known for producing quality drugs at an affordable price,” he said. “That is the major advantage for India and we are enjoying that for the last 15-20 years.”
Russia sales dip
India’s exports to Russia, however, have suffered because of the Ukraine war. Sales to the country fell 4.2 percent last fiscal year to $573 million, according to government data, taking Russia to the seventh position from fourth among India’s biggest pharma importers. Russia’s share in India’s pharma exports is generally around 2.5% but has now dipped to 2.2 percent.
Since Russia invaded Ukraine on February 24 last year and until June 5 this year, India’s pharma exports to Russia fell 4.6 percent to about $691 million from the corresponding period a year earlier, a government source told Reuters.
Bhaskar said the fall could be due to a dollar shortage for Russia, its attempts to prop up the domestic market and some reluctance among big Indian companies to do too much business with it while also trading with the United States, even though there are no Western sanctions on pharma products.










