‘Fire clouds’ over Arizona and Utah wildfires are creating their own erratic climate
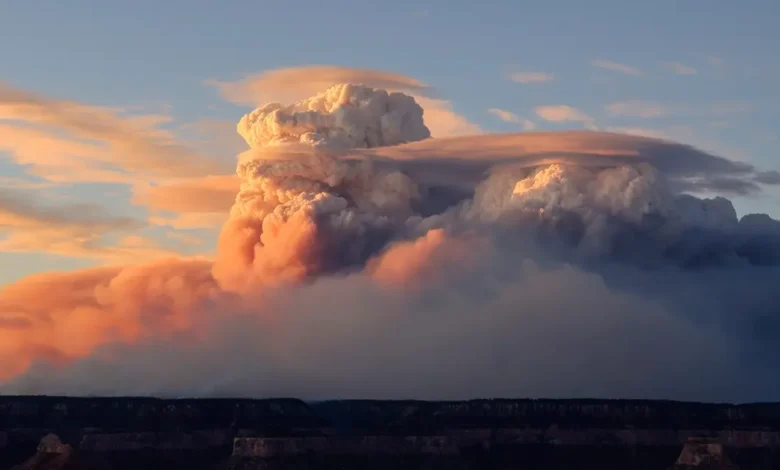

Two wildfires burning in the western United States – including one that has become a megafire on the North Rim of the Grand Canyon – are so hot that they’re spurring the formation of fire clouds that can create their own erratic weather systems.
In Arizona the wind-whipped wildfire that destroyed the Grand Canyon Lodge is 9 percent contained and has charred more than 164 square miles (424.7 square kilometers) to become the largest fire now burning in the continental US. Another large fire in Monroe Utah has burned 75 square miles (194 square kilometers) since July 13 and is 11 percent contained officials said Thursday. Evacuation orders were issued Wednesday for several towns in the fire’s path and scorched power poles caused electricity to be shut off in other nearby communities in south-central Utah.
Fire clouds present challenges for firefighters Towering convection clouds known as pyrocumulus clouds have been spotted over Arizona’s blaze for seven consecutive days fueling the fire with dry powerful winds fire information officer Lisa Jennings said. They form when air over the fire becomes super-heated and rises in a large smoke column. The billowing clouds can be seen for hundreds of miles and can look like an anvil or a dark spear jutting into the atmosphere. Their more treacherous big brother a fire-fueled thunderstorm known as the pyrocumulonimbus cloud sent rapid winds shooting out in all directions this week as a smoke column formed from the Utah fire then collapsed on itself said fire team information officer Jess Clark. “If they get high enough they can also create downdrafts and that’s something we really watch out for because that can quickly spread the fire and can be very dangerous for firefighters who are doing their work on the ground,” Jennings said.
Multiple fire crews in Utah were forced to retreat Wednesday as the unpredictable climate created by the clouds threatened their safety officials said. The same type of cloud which the National Aeronautics and Space Administration has dubbed “the fire-breathing dragon of clouds” recently formed a fire tornado that tore through an eastern Utah neighborhood with wind speeds estimated at 122 miles (196 kilometers) per hour.
Think of the fire as kind of like a hot air balloon so it adds buoyancy and things rise as a result said Derek Mallia an atmospheric scientist at the University of Utah who studies pyrocumulonimbus clouds and tracks fires in Utah and Arizona. You get this towering thunderstorm over the fire and just like any other thunderstorm it gets really windy underneath it. Because it’s the West these thunderstorms tend to be very dry. These clouds he said may appear more frequently as climate change causes a longer fire season drought conditions and extreme weather events.
Dry conditions fuel Grand Canyon megafire The Dragon Bravo Fire burning on the North Rim of the Grand Canyon was sparked by lightning on July 4. It was about a week later that conditions deteriorated with hot dry and windy weather helping to push the flames toward the Grand Canyon Lodge and the historic cabins that surround it.
The fire destroyed dozens of buildings and forced the closure of the national park’s North Rim for the rest of the season as hundreds of firefighters struggled to gain an upper hand. Thursday marked the eighth straight day of historically dry conditions Jennings said. Humidity levels have been in the single digits fuel moisture levels are extremely low and wind gusts were expected to crank up to 35 miles per hour (54.7 kilometers per hour). The pyrocumulus clouds have reached heights of at least 25000 feet (7620 meters) and fire behavior analyst Arthur Gonzales said they could go higher.
The direction of the wind has been fairly consistent for crews working the Dragon Bravo Fire and although they’ve been strong the predictability has allowed fire managers to more easily position crews on the fire lines. But when pyrocumulus clouds form and the winds become less predictable Jennings said firefighters often have to be pulled back to safety.
Fire prompts power outages in Utah Hot dry winds fanned the flames of the Monroe Canyon Fire on Thursday as firefighters worked to contain the spread. The fire has burned 12 power poles and many homes have been without electricity since Wednesday afternoon.
The National Weather Service issued red flag warnings for extreme fire danger in much of central and southwest Utah this week. In Antimony Utah 54 miles (87 kilometers) south of Monroe the town’s 123 residents were without power Thursday afternoon.
Mayor Kasey King who was helping people gather food and supplies at a community center said they could be without power for a week. The power company Garkane Energy Cooperative said it’s working to restore power as quickly as possible and has brought in backup generators.
Marnie Reynolds a resident of Antimony worried for the town’s many elderly residents. She has been using a camp stove to offer hot meals to neighbors and is using a generator to help people refrigerate groceries and medications. “We have been facing a lot of challenges but we have the best community,” she said.
In Richfield Utah 10 miles (16 kilometers) north of Monroe Lee Stevens said his yard was coated in ash. He and his wife who has asthma and is sensitive to the smoke have not yet been told to evacuate but are making preparations in case the fire spreads.
The National Interagency Fire Center in Idaho said Thursday that even with fewer acres having burned so far this year than average many parts of the country remain vulnerable to new starts and fast-moving flames.
___ Bryan reported from Albuquerque New Mexico.