Filling of Grand Renaissance Dam on the Nile complete, Ethiopia says
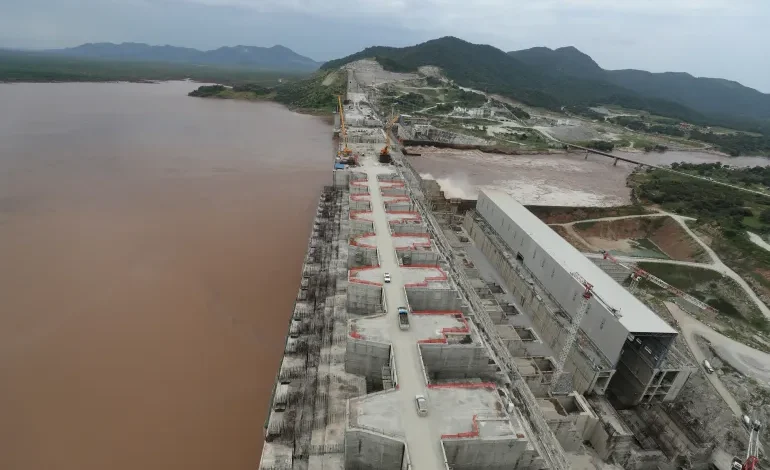

Ethiopia has announced that it has filled its Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) on the Nile, which has been the source of a long-running water dispute with downstream countries Egypt and Sudan.
The announcement on Sunday came just a fortnight after the three countries resumed negotiations, after a lengthy break, on an agreement that takes account of the water needs of all three.Egypt and Sudan fear the massive $4.2bn GERD will severely reduce the share of Nile water they receive and have repeatedly asked Addis Ababa to stop filling it until they have all reached agreement on how it should work.
“It is with great pleasure that I announce the successful completion of the fourth and final filling of the Renaissance Dam,” Ethiopia’s Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed said on X, formerly known as Twitter.
“There was a lot of challenge. We were many times dragged to go backwards. We had an internal challenge and external pressure. We’ve reached [this stage] by coping together with God,” Abiy said.
The Ethiopian government’s communications service said on X that GERD, arguably the largest dam in Africa, was “a gift to generations”.
“Today’s heroic generation will build tomorrow’s strong Ethiopia on a solid foundation,” it continued.
At full capacity, the huge hydroelectric dam – 1.8 kilometres (1.1 miles) long and 145 metres (476 feet) high – could generate more than 5,000 megawatts.
That would double Ethiopia’s production of electricity, to which only half the country’s population of 120 million currently has access.‘Illegal announcement’
The Egyptian foreign ministry condemned as “illegal” Ethiopia’s announcement that it had filled the dam on the Nile.
‘Illegal announcement’
The Egyptian foreign ministry condemned as “illegal” Ethiopia’s announcement that it had filled the dam on the Nile.
Egypt, which is already suffering from severe water scarcity, sees the dam as an existential threat because it relies on the Nile for 97 percent of its water needs.
The position of fragile Sudan, which is currently mired in a civil war, has fluctuated in recent years.
Ethiopia has said the GERD, which is in the northwest of the country around 30km (19 miles) from the border with Sudan, will not reduce the volume of water flowing downstream.
The United Nations says Egypt could “run out of water by 2025” and parts of Sudan, where the Darfur conflict was essentially a war over access to water, are increasingly vulnerable to drought as a result of climate change.