Boeing 737 Max 9: United Airlines finds loose bolts during inspections

Bolts in need of “additional tightening” have been found during inspections of Boeing 737 Max 9s, United Airlines has said.
Inspections began after a section of the fuselage fell from an Alaska Airlines 737 Max 9 on Friday.
United Airlines said “installation issues” relating to door plugs would be “remedied” before the aircraft type would return to service.
Some 171 planes of the same type remain grounded by the US regulator.
In its statement, United said: “Since we began preliminary inspections on Saturday, we have found instances that appear to relate to installation issues in the door plug – for example, bolts that needed additional tightening.”
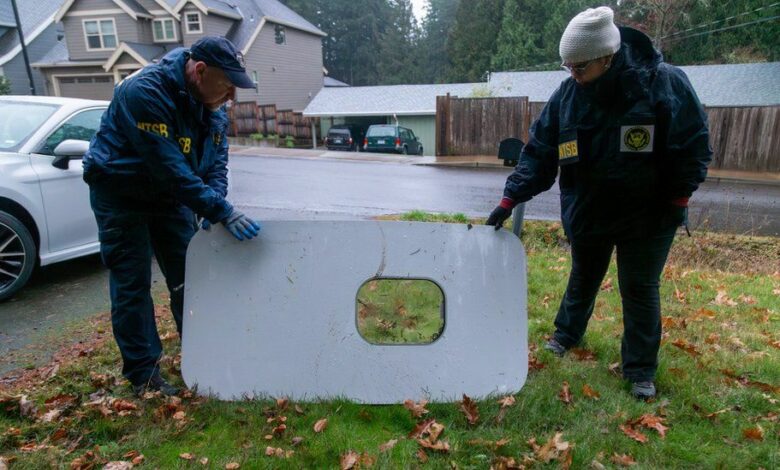
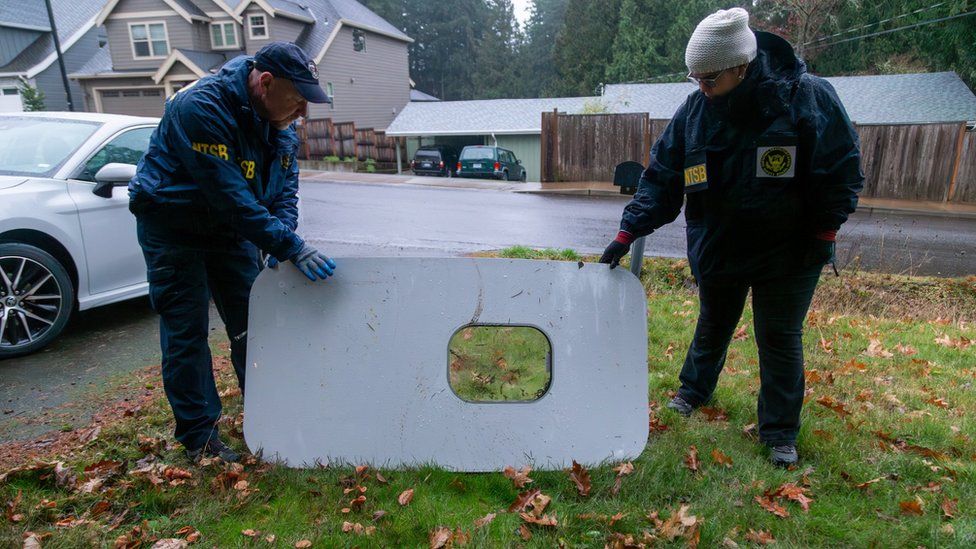
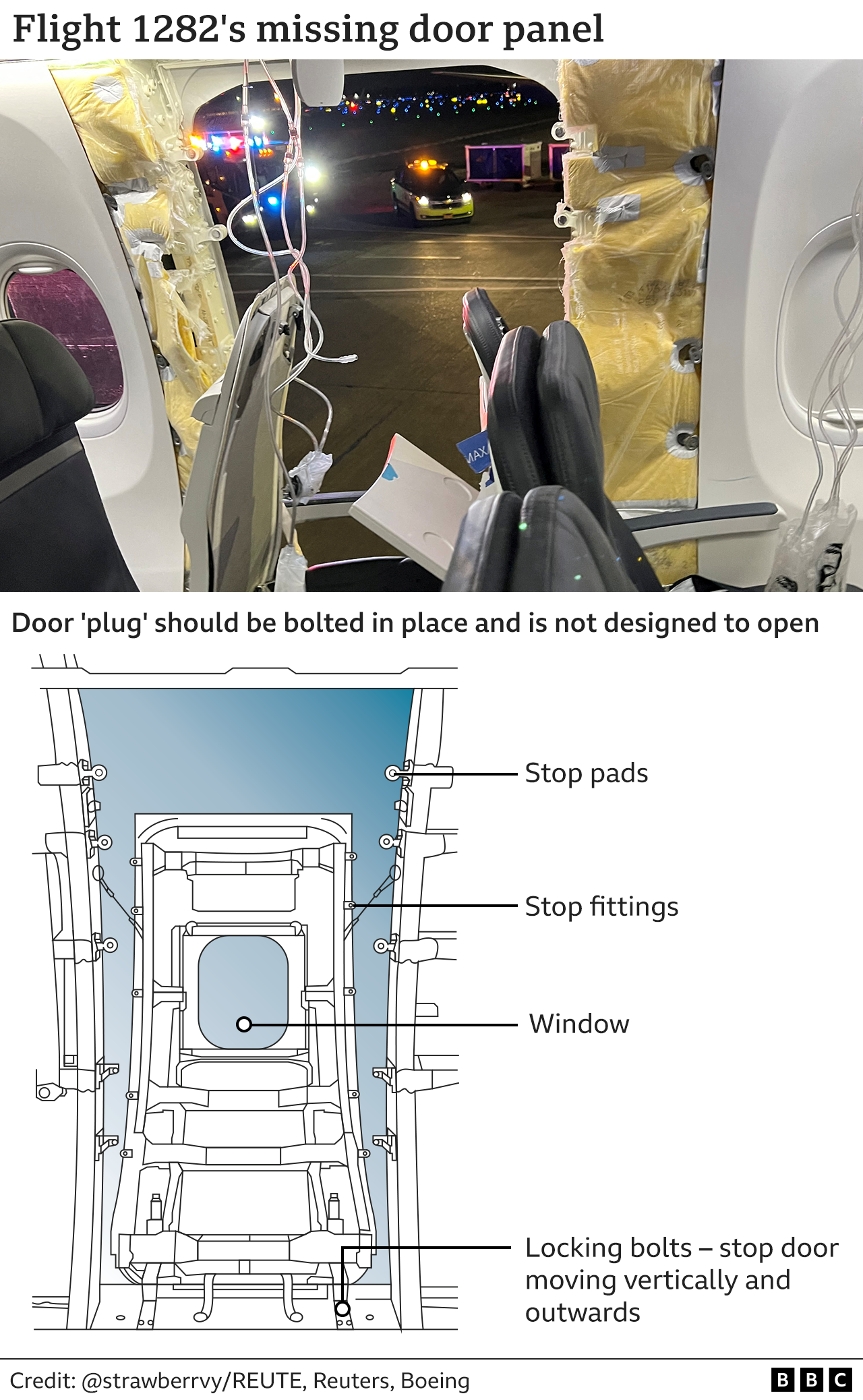
The door plug is a piece of fuselage with a window that can be used as an emergency exit in certain configurations.
It was this part of the Alaska Airlines plane which dramatically fell off mid-flight over the US state of Oregon, eventually landing in a teacher’s back garden.
The plane made an emergency landing and none of the passengers were injured.
The vast majority of Boeing 737 Max 9s used in the US are operated by United Airlines and Alaska, while Turkish Airlines, Panama’s Copa Airlines and Aeromexico have also grounded jets of the same model for inspections.

United said it had cancelled 200 flights as of Monday and expected significant cancellations on Tuesday.
“We have been able to operate some planned flights by switching to other aircraft types, avoiding about 30 cancellations each on Monday and Tuesday,” United added.
Meanwhile on Monday, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), which regulates air travel in the US, said it had provided a checklist for operators to adhere to during inspections.
In a statement, the FAA said all 737 Max 9 aircraft would remain grounded until operators “complete enhanced inspections which include both left and right cabin door exit plugs, door components, and fasteners”.
“Operators must also complete corrective action requirements based on findings from the inspections prior to bringing any aircraft back into service,” the statement added.
Flight 1282 reached 16,000ft (4.8km) when it began its emergency descent on Friday evening, according to flight tracking data.
Images shared online – and later by investigators – showed a wide hole in the side of the craft, with oxygen masks dangling from the ceiling.
Passengers were quoted by The Oregonian newspaper as saying that a young boy seated near the affected area had his shirt ripped off by the force of the decompression.
The US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), which is leading an investigation into the incident, said pilots had reported pressurisation warning lights on three previous flights made by the specific Alaska Airlines Max 9 involved in the incident.
The jet had been prevented from making long-haul flights over water so that the plane “could return very quickly to an airport” in the event the warnings happened again, NTSB chief Jennifer Homendy said.
It is not clear if there is a link between the issues that led to those warnings, and the issue that caused the blowout on 5 January.
Alaska Airlines said in its most recent statement: “While we await the airworthiness directive (AD) inspection criteria from the FAA and Boeing, our maintenance teams are prepared and ready to perform the required inspections of the mid exit door plugs on our 737-9 Max fleet.
“The 737-9 Max grounding has significantly impacted our operation. We have cancelled 170 Sunday flights and 60 cancellations for Monday, with more expected.”
Boeing said in a statement: “Safety is our top priority and we deeply regret the impact this event has had on our customers and their passengers.”
The company’s 737 Max has been described as “the most scrutinised transport aircraft in history” after a series of safety issues.
In late 2018 and early 2019, two of its aircraft were lost in near identical incidents, off the coast of Indonesia and outside the Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa.
A total of 346 people were killed. Both crashes were caused by flawed flight control software, which ultimately forced the planes into catastrophic dives, despite the best efforts of the pilots.










